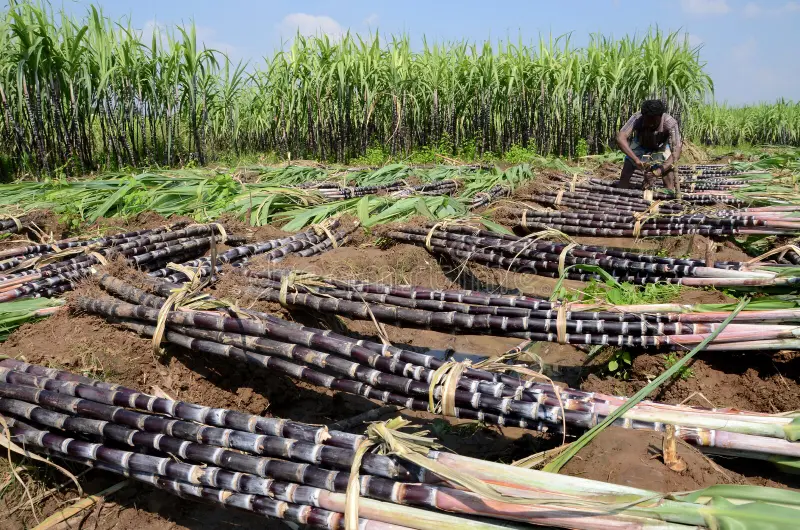
New Delhi, March 26, 2025 – India, the world's second-largest producer of sugar, has recently announced that it will allow the export of 1 million metric tons of sugar for the current season. This decision marks a significant policy shift after earlier concerns about lower output forecasts raised doubts about the feasibility of exports. With adequate stock levels to meet domestic consumption and ethanol production needs, the government has assured stakeholders that exports will not disrupt local availability.
Background of India's Sugar Industry
India is a key player in the global sugar industry, competing with countries like Brazil and Thailand. The country produces millions of tons of sugar annually, with Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh being the leading contributors. The sugar industry is deeply intertwined with the Indian economy, supporting millions of farmers and contributing significantly to exports.
Sugar production in India is influenced by monsoon patterns, government policies, and market demand. Fluctuations in output often prompt the government to adjust its trade policies, either restricting or encouraging exports depending on the domestic scenario.
Why Was Sugar Export Initially Limited?
At the beginning of the 2024-25 season, there were concerns about lower sugarcane yields due to irregular monsoons and unfavorable weather conditions. The government, wary of potential shortages, initially restricted exports to prioritize domestic supply and ethanol blending programs. Ethanol production is a key focus for India’s energy security strategy, as it aims to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels by blending ethanol with petrol.
However, recent assessments have indicated that domestic stock levels are stable, prompting the government to allow controlled exports.
Impact of the Export Policy Change
1. Domestic Market Stability
One of the primary concerns when permitting sugar exports is ensuring that domestic prices remain stable. The government has emphasized that the decision to allow exports is based on careful stock assessments, ensuring that Indian consumers will not face price hikes.
2. Benefits for Sugar Mills and Farmers
Permitting exports benefits sugar mills, which often struggle with excess stockpiles. By exporting 1 million metric tons, mills can reduce their surplus, generate revenue, and clear payments to sugarcane farmers. This move is expected to ease financial stress on the industry, which has been grappling with delayed payments and liquidity constraints.
3. Boost to International Trade and Economy
India’s sugar exports contribute to the country’s foreign exchange earnings. With global sugar prices currently favorable, this move enables Indian sugar producers to take advantage of high demand in international markets, especially in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
4. Ethanol Production and Sustainability Goals
Despite permitting sugar exports, India remains committed to its ethanol blending targets. The government has reassured that sufficient sugarcane will be available for ethanol production, a crucial component of India's renewable energy strategy. The country aims to achieve 20% ethanol blending by 2025, reducing its dependence on imported crude oil and promoting cleaner energy alternatives.
Global Market Implications
India's decision to allow sugar exports will have a ripple effect on global markets. Major importers such as Indonesia, Bangladesh, and the United Arab Emirates are expected to benefit from increased supply. Additionally, global sugar prices, which have been volatile due to production concerns in Brazil and Thailand, might stabilize with India's contribution to the market.
However, experts caution that if India faces any unexpected production shortfalls later in the season, it may have to reconsider its export policy to maintain domestic stability.
Challenges and Risks
Despite the positive outlook, there are potential challenges associated with the export decision:
- Climate Uncertainty: Unpredictable weather conditions could impact future sugarcane production, leading to possible shortages.
- Ethanol vs. Sugar Dilemma: Balancing sugar availability for both exports and ethanol production requires careful policy execution.
- Market Competition: Countries like Brazil dominate sugar exports, and India must ensure competitive pricing to maintain its share in the global market.
Conclusion
India’s decision to allow sugar exports while ensuring domestic stability showcases its strategic approach to trade policy. By carefully monitoring stock levels and global market trends, the government aims to benefit farmers, sugar mills, and international trade partners. However, maintaining a balance between exports, domestic consumption, and ethanol production will be key to sustaining long-term growth in the sugar industry.
As global demand for sugar continues to rise, India's role in the international market remains crucial. The latest policy decision reinforces India's position as a significant player in the sugar trade, with a strong focus on economic and energy sustainability. Future policy adjustments will depend on evolving market conditions and production forecasts, making it a sector to watch closely in the coming months.